Painful Movable Lump In Breast – Fibrocystic change is the most common cause of breast tumors in women aged 30–50 years. The changes occur because some breast tissue overreacts to the normal monthly changes in hormone levels. It can cause scarring around the tubes, which can block the tube and form small cysts. Lumps are soft and mobile. Breast tenderness or pain is common and may be generalized or felt, especially in the upper, outer part of the breasts (near the armpits).
Lumps vary in size during the menstrual cycle and sometimes green or brown nipple discharge occurs spontaneously (without pressure).
Painful Movable Lump In Breast
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/understanding-breast-lumps-both-benign-and-cancerous-430415-5c2fda3b4cedfd0001ef3491.png?strip=all)
Fibrocystic breast changes do not require any treatment if the discomfort is mild. Moderate discomfort can be managed by wearing a properly fitting bra and pain medication such as paracetamol. Sometimes large cysts that cause severe pain may require aspiration (a doctor uses a needle and syringe to remove fluid).
Stomach Hurting? Causes Of Abdominal Pain
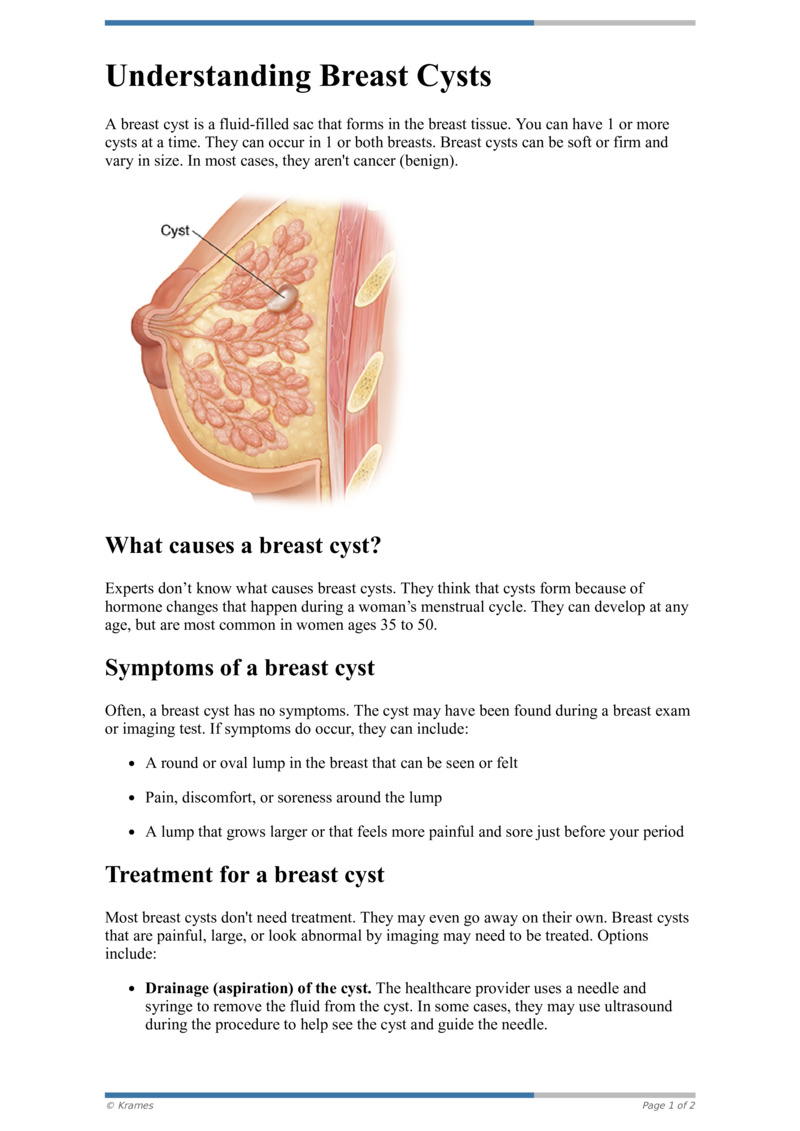
Breast cysts are fluid-filled sacs. You may have a single cyst or multiple cysts. Cysts can occur naturally as the breast changes with age due to normal changes in estrogen hormone levels. During the menstrual cycle, estrogen creates fluid. Although you can develop breast cysts at any age, they are most common in women over 35.
After menopause (when your periods stop), estrogen levels decrease, and cysts usually don’t form. Women on HRT can still get cysts. They may be too small to feel and be detected only on imaging, or they may be large enough to feel like a lump. Large cysts can press on other tissues in the breast and cause discomfort.
Clinical examination alone cannot reliably diagnose cysts. An ultrasound can confirm whether the lump is solid or cystic (fluid-filled) and should be done before the cyst is drained.
Simple breast cysts are usually left alone. Sometimes an ultrasound does not show the appearance of normal breast cysts, and a needle biopsy may be necessary to confirm that they are breast cysts. If simple breast cysts are too uncomfortable, they can be drained to relieve pain. Sometimes they can be refilled or reversed.
Lump On Chest Wall
Sebaceous cysts form in the sebaceous glands, which secrete sebum, the oil that coats the hair and skin. They are most often found on the face, back and neck, but are also very common on the skin of the chest. Cysts are often surgically removed for cosmetic reasons, and they can become recurrently infected.
It is a painless soft tumor resulting from the overgrowth of fibrous, glandular and adipose tissue in a thin capsule of connective tissue. In some cases, this can lead to breast enlargement without feeling a local lump. It is usually detected on mammography, but a biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis. Not to be confused with a hematoma, a pool of clotted blood in tissue.
These are benign fatty lumps or lumps, fat cells found anywhere in the body and sometimes found in the breast. They are painless, mobile tumors and usually do not require treatment unless they develop symptoms or show signs of growth.

Fat necrosis: V. S. Upadhyaya, R. Upbur and L. Mammographic and Sonographic Features of Fat Necrosis of the Breast by Shetty is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0. This image was cropped from the original.
Signs Of Breast Cancer To Bring To Your Doc’s Attention
It results from damage to the fat cells in the breast caused by trauma such as a car accident, surgery, radiation therapy, or blood-thinning medications.
Blood supply to fat cells is blocked, causing cell damage or cell death. It can be felt as a lump or seen on a mammogram or ultrasound scan. Sometimes cysts containing oil can form in the area of fat necrosis.
Fat necrosis can look like cancer on a mammogram, so the doctor may want to take a sample (biopsy). Usually, no treatment is needed and fat necrosis resolves on its own.
Fibroadenomas are usually a lump or change detected on an ultrasound/mammogram. Fibroadenomas can vary in size, with some women having more than one. The only way to know if you have a fibroadenoma is to take a sample (biopsy).
Common Breast Cancer Myths You Should Burst. Busted!
Fibroadenomas are common and are thought to be related to the female hormone estrogen. Hormone levels are high when we are young, pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking hormone replacement medications. Although these can occur at any age, they are more likely to occur between the ages of 15-40.
Fibroids are found in the breast lobule, the part of the breast that produces milk. The lobules are made up of glands (which hold the milk), ducts (which carry milk away from the breast) and fibrous tissue (which keeps the breast in shape). Fibroadenomas occur when the tissue in the lobule grows larger and hardens.
Most will shrink over time, so they are usually left alone. If your fibroadenoma is enlarged or painful, you should talk to a breast specialist about having it removed. Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare, fast-growing cancer that requires immediate treatment. It causes symptoms similar to a breast infection. Symptoms of IBC include redness, swelling, pain, an orange peel-like breast, and enlargement of the breast skin. Treatment includes chemotherapy, surgery and radiation.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breast-exam-GettyImages-881118412-b35d26af89c14154aee46dd3a8b98697.jpg?strip=all)
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare type of cancer that spreads rapidly. Unlike most breast cancers, IPC does not usually cause lumps in the breast tissue. Instead, it appears as a rash, forming an orange peel-like skin texture on the affected breast. IBC causes pain, redness, swelling and tenderness in the affected breast.
Lump In Breast – Cancer Or Benign Cysts In Young Women
IBC results when cancer cells block the lymphatic vessels — the small, hollow tubes that allow lymph fluid to leave your breast. The blockage leads to inflammation and thus symptoms, making it easy to mistake IPC for infection.
IBC grows rapidly and requires immediate treatment. Health care providers typically treat IPC with chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy.
Cleveland Clinic is a not-for-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse any non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Politics
Inflammatory breast cancer occurs at different rates worldwide. It is most common in North Africa. It accounts for 4% of breast cancer cases in Tunisia and 11% of breast cancer diagnoses in Egypt. IPC is rare in the United States, accounting for only 1% to 5% of breast cancer cases.
Causes Of Lumps On The Neck
Inflammatory breast cancer is challenging to catch because it often does not cause a lump like the more common forms of breast cancer. Instead, the first symptoms are related to swelling (redness, swelling, pain) of your affected breast. These symptoms make it easy to mistake IBC for a less serious condition, such as an infection.
Most inflammatory breast cancer is considered invasive ductal carcinoma. “Ductal” carcinoma is cancer that originates from the cells that line your milk ducts. “Invasive” ductal carcinoma is cancer that spreads beyond your milk ducts and invades healthy tissue. Researchers do not know what causes these cells to become malignant (cancerous).
Inflammatory breast cancer develops when cancer cells block lymph vessels. Lymphatic vessels are hollow tubes in your lymphatic system that allow lymph fluid to leave your breast. Bloating can make your breasts red, swollen, and swollen. In most cases of IBC, the cancer cells spread (metastasize) outward from your lymph vessels. Metastasized cancer affects your other organs and is more difficult to treat.

Inflammatory breast cancer is rare, with symptoms similar to a more common condition – breast infections (mastitis). Your health care provider may prescribe antibiotics and see if that resolves your symptoms to rule out an infection. If they suspect IBC, they will order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond your breast.
Lump In Breast
Biopsy results can help your healthcare provider diagnose cancer or determine whether it has spread outside of your breast tissue. If IBC is diagnosed, it is stage III or stage IV. Stage III cancer has only spread to your breast tissue. Stage IV cancer has spread to other organs.
Depending on the characteristics of your cancer cells (found during biopsy), you may receive treatments such as targeted therapy, hormone therapy, or immunotherapy.
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you participate in a clinical trial. A clinical trial is a study that tests the safety and effectiveness of a new cancer treatment. Treatments that are successful in clinical trials often become standard treatment approaches.
Treatment for IPC can cause complications such as lymphadenopathy (buildup of lymph fluid) after surgery to remove your lymph nodes.
Moving On Abc
Because IBC develops so quickly, the cancer has usually spread to other tissues (metastases) by the time it is diagnosed. You may need additional treatments if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
You can’t prevent inflammatory breast cancer. For best results, seek early treatment. Tell your healthcare provider as soon as possible about any breast changes.
IBC is considered a fast-growing (aggressive) cancer. It only takes a few weeks or months to progress. If it is detected, it already exists

Very painful lump in breast, non movable lump in breast, painful lump in men's breast, movable lump in breast, movable painful lump in breast, painful lump in breast male, sudden painful lump in breast, painful lump in breast, painful large lump in breast, movable lump in breast no pain, non painful lump in breast, painful lump in breast female